unmaintainable code 如何写出无法维护的代码 - 伪装欺诈
Camouflage 伪装欺诈
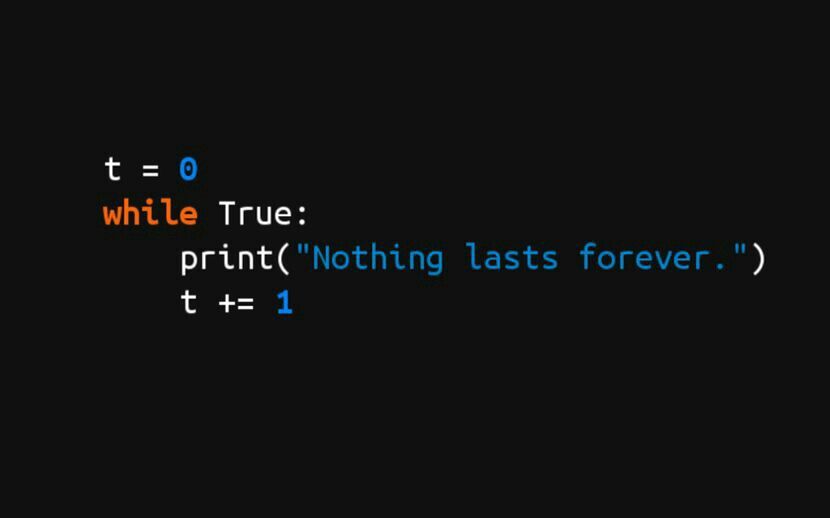
The longer it takes for a bug to surface, the harder it is to find.
漏洞出现的时间越长,发现就越难。
Roedy 罗迪
Much of the skill in writing unmaintainable code is the art of camouflage, hiding things, or making things appear to be what they are not. Many depend on the fact the compiler is more capable at making fine distinctions than either the human eye or the text editor. Here are some of the best camouflaging techniques.
编写无法维护代码的技巧很大程度上在于伪装、隐藏事物或让事物看起来并非真实的艺术。许多问题依赖于编译器比人眼或文本编辑器更擅长细分。以下是一些最佳的伪装技巧。
Write Efficient Code 编写高效的代码
We should forget about small efficiencies, say about 97% of the time; premature optimization is the root of all evil.
我们应该忘记那些小的效率,比如大约 97% 当时;过早优化是万恶之源。
Donald Ervin Knuth 唐纳德·欧文·克努斯
More computing sins are committed in the name of efficiency (without necessarily achieving it) than for any other single reason — including blind stupidity.
以效率之名(不一定能实现效率)犯下的计算罪行比任何其他单一原因都多——包括盲目愚蠢。
W. A. Wulf 沃尔夫
The safest way to disguise your obfuscation work then is to make it look as if your motive for it is making the program run faster.
掩饰混淆工作最安全的方法是让你看起来像是为了让程序运行更快。
Code That Masquerades As Comments and Vice Versa 代码伪装成注释,反之亦然
1 | for ( j=0; j<array_len; j+ =8 ) |
Without the colour coding, would you notice that three lines of code are commented out?
:包含代码部分 这部分被注释了,但乍一看似乎并没有。 如果没有颜色编码,你会注意到有三行代码被注释了吗 出去?
namespaces 命名空间
: Struct/union and typedef struct/union are different name spaces in C (not in C++). Use the same name in both name spaces for structures or unions. Make them, if possible, nearly compatible.
: struct/union 和 typedef struct/union 是不同的命名空间 在 C 语言中(而非 C++ 语言)。 在两个命名空间中,结构或联合体都使用相同名称。如果 有可能,几乎兼容。
1 | typedef struct { |
Hide Macro Definitions 隐藏宏定义
: Hide macro definitions in amongst rubbish comments. The programmer will get bored and not finish reading the comments thus never discover the macro. Ensure that the macro replaces what looks like a perfectly legitimate assignment with some bizarre operation, a simple example:
:把宏定义藏在垃圾评论里。程序员会感到无聊,看不完评论,因此永远找不到宏。确保宏用一些奇怪的作替换看似完全合法的赋值,举个简单的例子:
1 |
Look Busy 看起来忙碌
: use define statements to make made up functions that simply comment out their arguments, e.g.:
: 使用定义语句来创建仅注释其参数的函数,例如:
1 |
|
Use Continuation to hide variables 使用延续来隐藏变量
: Instead of using
: 而不是使用
1 |
break up xy_z onto two lines:
把 xy_z 分成两条线:
1 |
That way a global search for xy_z will come up with nothing for that file. To the C preprocessor, the \ at the end of the line means glue this line to the next one.
这样全局搜索 xy_z 就不会找到该文件的任何信息。对 C 预处理器来说,行尾的 \ 表示将这行粘接到下一个行。
Arbitrary Names That Masquerade as Keywords 伪装成关键词的任意名称
: When documenting and you need an arbitrary name to represent a filename use file . Never use an obviously arbitrary name like Charlie.dat or Frodo.txt. In general, in your examples, use arbitrary names that sound as much like reserved keywords as possible. For example, good names for parameters or variables would be: bank, blank, class, const, constant, input, key, keyword, kind, output, parameter parm, system, type, value, var and variable . If you use actual reserved words for your arbitrary names, which would be rejected by your command processor or compiler, so much the better. If you do this well, the users will be hopelessly confused between reserved keywords and arbitrary names in your example, but you can look innocent, claiming you did it to help them associate the appropriate purpose with each variable.
:在记录时,你需要 任意名称表示文件名时,使用文件 。切勿使用明显随意的名字,比如 Charlie.dat 或 Frodo.txt。一般来说,在你的例子中,使用听起来尽可能像保留关键词的任意名称。例如,参数或变量的好名称包括:bank, blank, class, const, constant, input, key, keyword, kind, output, parameter parm, system, type, value, var and variable 和变量 .如果你用实际保留词来命名任意名称,而这些词会被命令处理器或编译器拒绝,那就更好了。如果你做得好,用户会在你示例中对保留关键词和任意名称感到极度困惑,但你可以装作无辜,声称这是为了帮助他们与每个变量关联到合适的目的。
Code Names Must Not Match Screen Names 代号不得与屏幕名匹配
: Choose your variable names to have absolutely no relation to the labels used when such variables are displayed on the screen, e. g. on the screen label the field Postal Code but in the code call the associated variable zip.
:选择你的变量名 与显示此类变量时所用标签完全无关 例如,屏幕上标记该字段为邮政编码 ,但在代码中调用相关变量 zip。
Don’t Change Names 别改名字
: Instead of globally renaming to bring two sections of code into sync, use multiple TYPEDEFs of the same symbol.
:与其全局重命名以同步两个代码段,不如使用同一符号的多个 TYPEDEF。
How to Hide Forbidden Globals 如何隐藏禁忌全局
: Since global variables are evil, define a structure to hold all the things you’d put in globals. Call it something clever like EverythingYoullEverNeed. Make all functions take a pointer to this structure (call it handle to confuse things more). This gives the impression that you’re not using global variables, you’re accessing everything through a handle. Then declare one statically so that all the code is using the same copy anyway.
:既然全局变量是邪恶的,请定义一个结构来容纳你在全局变量中放置的所有内容。可以叫它一个聪明点的名字,比如《你永远需要的一切》。让所有函数都指向这个结构(叫它 handle,这样会更复杂)。这给人一种感觉,你没有使用全局变量,而是通过一个句柄访问所有内容。然后静态声明一个,这样所有代码都使用同一个副本。
Hide Instances With Synonyms 隐藏带有同义词的实例
: Maintenance programmers, in order to see if they’ll be any cascading effects to a change they make, do a global search for the variables named. This can be defeated by this simple expedient of having synonyms, such as
维护程序员为了判断这些变量是否会对他们所做的更改产生连锁反应,会对所命名的变量进行全局搜索。这一点可以通过使用同义词来解决,例如
1 |
These defs should be scattered through different include-files. They are especially effective if the include-files are located in different directories. The other technique is to reuse a name in every scope. The compiler can tell them apart, but a simple minded text searcher cannot. Unfortunately SCIDs in the coming decade will make this simple technique impossible. since the editor understands the scope rules just as well as the compiler.
这些 defs 应该分散在不同的包含文件中。当包含文件位于不同的目录中时,它们尤其有效。另一种方法是在每个范围中重复使用同一个名字。编译器可以区分它们,但简单的文本搜索者做不到。不幸的是,未来十年的 SCID 将使这一简单技术变得不可能。因为编辑器和编译器一样理解作用域规则。
Long Similar Variable Names 长而相似的变量名称
: Use very long variable names or class names that differ from each other by only one character, or only in upper/lower case. An ideal variable name pair is swimmer and swimner. Exploit the failure of most fonts to clearly discriminate between ilI1| or oO08 with identifier pairs like parselnt and parseInt or D0Calc and DOCalc. l is an exceptionally fine choice for a variable name since it will, to the casual glance, masquerade as the constant 1. In many fonts rn looks like an m. So how about a variable swirnrner. Create variable names that differ from each other only in case e.g. HashTable and Hashtable.
:使用非常长的变量名或类名 它们之间仅差一个字符,或仅在大写/小写上有所不同。一个 理想的变量名称对是游泳者和游泳者 。利用大多数字体无法明确区分 ilI1| 或 oO08 的缺陷,识别码对如 蛇佬腔和语法分析直译 D0 微积分和 DOCalc。L 是变量名的绝佳选择,因为它乍看之下会伪装成常数 1。现在很多字体看起来像是 m。那么,变速器怎么样?创建变量名仅在 HashTable 和 Hashtable 等情况下不同。
Similar-Sounding Similar-Looking Variable Names 发音相似、外观相似的变量名称
: Although we have one variable named xy_z, there’s certainly no reason not to have many other variables with similar names, such as xy_Z, xy__z, _xy_z, _xyz, XY_Z, xY_z and Xy_z.
:虽然我们有一个变量名为 xy_z,但完全没有理由不拥有许多其他类似名称的变量,比如 xy_Z、xy__z、_xy_z、_xyz、XY_Z、xY_z 和 Xy_z。
Variables that resemble others except for capitalization and underlines have the advantage of confounding those who like remembering names by sound or letter-spelling, rather than by exact representations.
除了大写和下划线外,其他变量相似的变量,有个优势是让那些喜欢通过发音或字母拼写记住名字而非精确表示的人感到困惑。
Overload and Bewilder 重载与迷惑
: In C++, overload library functions by using #define. That way it looks like you are using a familiar library function where in actuality you are using something totally different.
在 C++ 中,通过使用 #define 来超载库函数。这样看起来就像你在用一个熟悉的库函数,实际上你用的是完全不同的东西。
Choosing The Best Overload Operator 选择最佳重载
: In C++, overload +,-,*,/ to do things totally unrelated to addition, subtraction etc. After all, if the Stroustroup can use the shift operator to do I/O, why should you not be equally creative? If you overload +, make sure you do it in a way that i = i + 5; has a totally different meaning from i += 5; Here is an example of elevating overloading operator obfuscation to a high art. Overload the ‘!’ operator for a class, but have the overload have nothing to do with inverting or negating. Make it return an integer. Then, in order to get a logical value for it, you must use ‘! !’. However, this inverts the logic, so [drum roll] you must use ‘! ! !’. Don’t confuse the ! operator, which returns a boolean 0 or 1, with the ~ bitwise logical negation operator.
在 C++ 中,可以超载+,-,*,/来完成与加法、减法等完全无关的事情。毕竟,如果 Stroustroup 能用移位做 I/O,为什么你们不能同样有创造力呢?如果你超载+,确保以 i = i + 5 的方式来实现;这与 i += 5 的含义完全不同;这里有一个将重载算子混淆提升到高深技艺的例子。让一个类的“!”运子重载,但这个重载与反转或否定无关。让它返回整数。然后,为了获得逻辑值,你必须使用“!!”。然而,这会颠倒逻辑,所以[鼓声]你必须使用“!!”。别混淆!算符,返回布尔 0 或 1,且按位逻辑否定算子为~。
Overload new 重载 new
: Overload the new operator - much more dangerous than overloading the +-/*. This can cause total havoc if overloaded to do something different from it’s original function (but vital to the object’s function so it’s very difficult to change). This should ensure users trying to create a dynamic instance get really stumped. You can combine this with the case sensitivity trick: also have a member function and variable called New.
:给新重载——太多 比重载+-/*更危险。如果重载,可能会造成彻底的混乱 做一些与其原始功能不同的事(但对 对象的功能非常难更改)。这应该能确保 用户试图创建动态实例时会非常困惑。你可以把这些结合起来 使用大小写区分技巧:还存在一个成员函数和变量,称为 New 。
#define
: #define in C++ deserves an entire essay on its own to explore its rich possibilities for obfuscation. Use lower case #define variables so they masquerade as ordinary variables. Never use parameters to your preprocessor functions. Do everything with global #defines. One of the most imaginative uses of the preprocessor I have heard of was requiring five passes through CPP (C++) before the code was ready to compile. Through clever use of defines and ifdefs, a master of obfuscation can make header files declare different things depending on how many times they are included. This becomes especially interesting when one header is included in another header. Here is a particularly devious example:
: #define C++ 值得单独写一篇文章来探讨其丰富的混淆可能性。使用小写的 #define 变量,使其伪装成普通变量。千万不要用参数来控制你的预处理器功能。所有事情都用全局 #defines。我听说过的预处理器最有创意的用途之一是代码编译前需要经过五次 CPP(C++)程序。通过聪明 使用定义和 IFDEF,混淆大师可以使头文件声明 根据被包含的次数不同,内容也会有所不同。这变成了 当一个头部被包含在另一个头部时,这一点尤其有趣。这里有一个 特别狡猾的例子:
1 |
|
This one gets fun when passing g() a char* because a different version of g() will be called depending on how many times the header was included.
这个方法在传递 g() 字符* 时会很有趣,因为根据头部被包含的次数,会调用不同版本的 g()。
Compiler Directives 编译器指令
: Compiler directives were designed with the express purpose of making the same code behave completely differently. Turn the boolean short-circuiting directive on and off repeatedly and vigourously, as well as the long strings directive.
编译器指令的设计明确目的是让同一代码完全不同的行为。反复且有力地开关布尔短路指令,以及长字符串指令。
Red Herrings 掩人耳目(红鲱鱼)
Pepper your code with variables that are never used and methods that are never called. This is most easily done by failing to remove code that is no longer used. You can save the code on grounds someday it may need to be revived. You get bonus points if these drone variables and methods have names similar to actual worker ones. The maintenance programmer will inevitably confuse the two. Changes made to drone code will happily compile, but have no effect.
在代码中加入从未被使用过的变量和从未调用的方法。这最简单的方法是不删除不再使用的代码。你可以保存代码,以防有一天需要恢复。如果这些无人机变量和方法的名字和实际工人类似,那你会加分。维护程序员不可避免地会混淆这两者。对无人机代码所做的修改会愉快地编译,但不会有影响。
- 标题: unmaintainable code 如何写出无法维护的代码 - 伪装欺诈
- 作者: Spike Zhang
- 创建于 : 2026-02-10 10:11:42
- 更新于 : 2026-02-10 10:13:25
- 链接: https://chaosbynn.github.io/2026/02/10/unmaintainable-code-如何写出无法维护的代码-伪装欺诈/
- 版权声明: 本文章采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 进行许可。